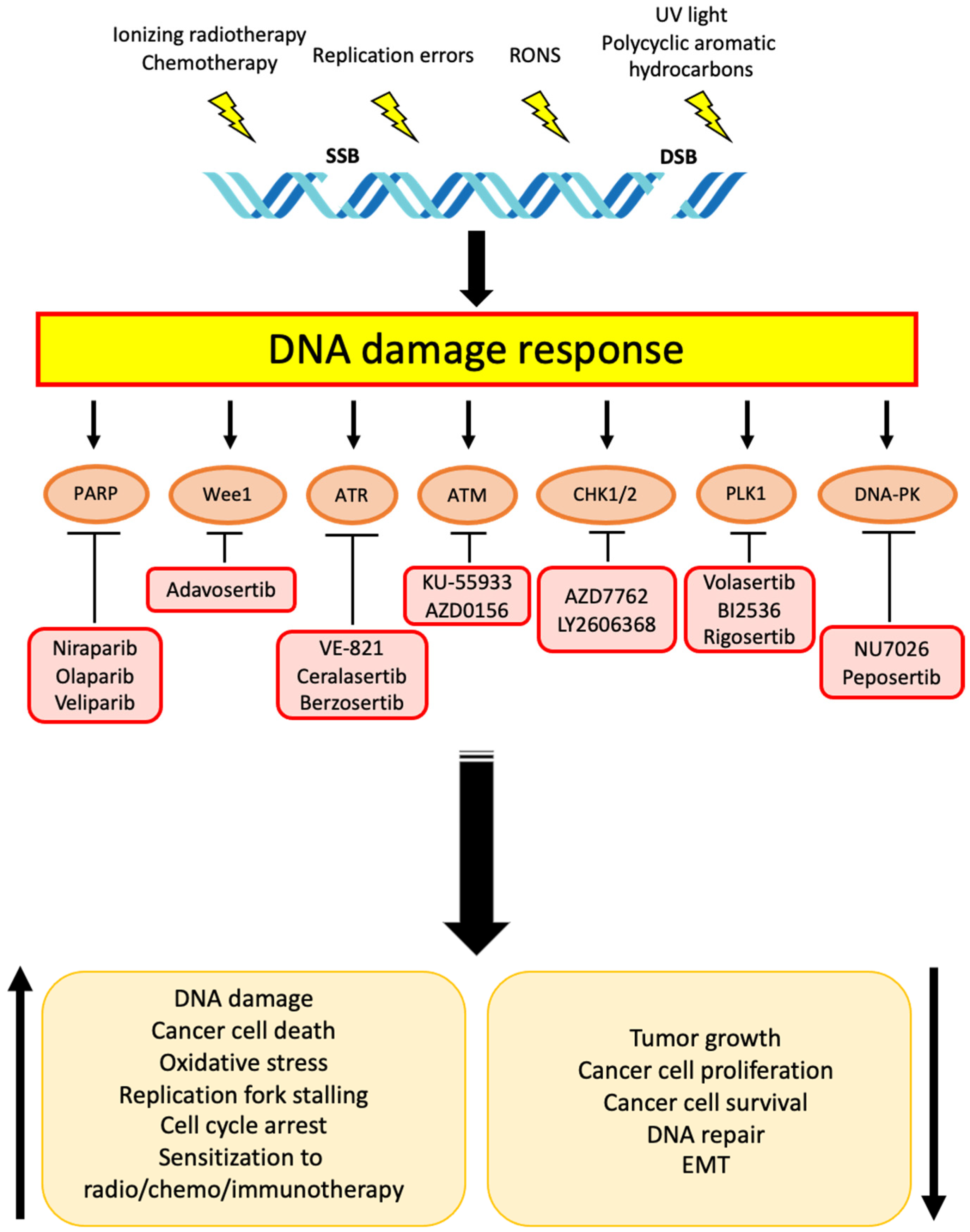
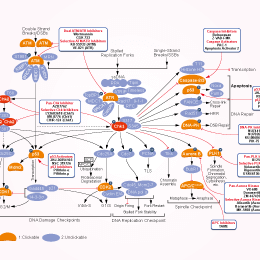
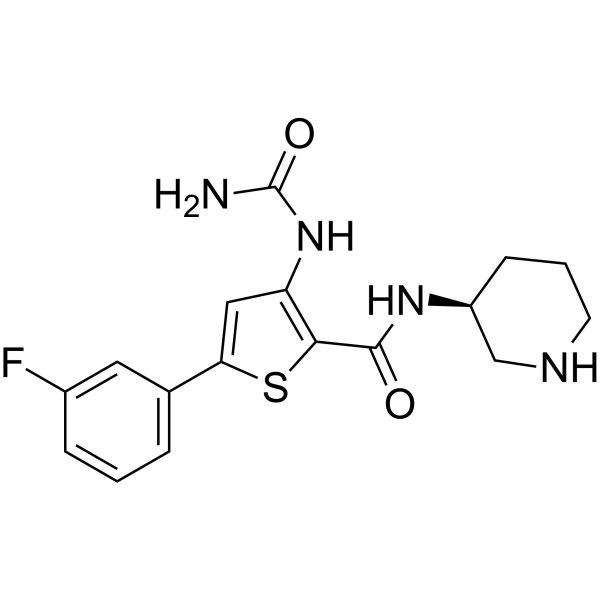
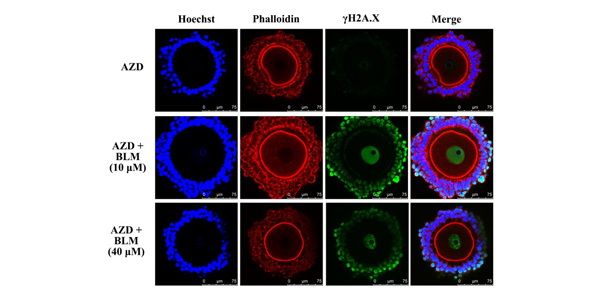
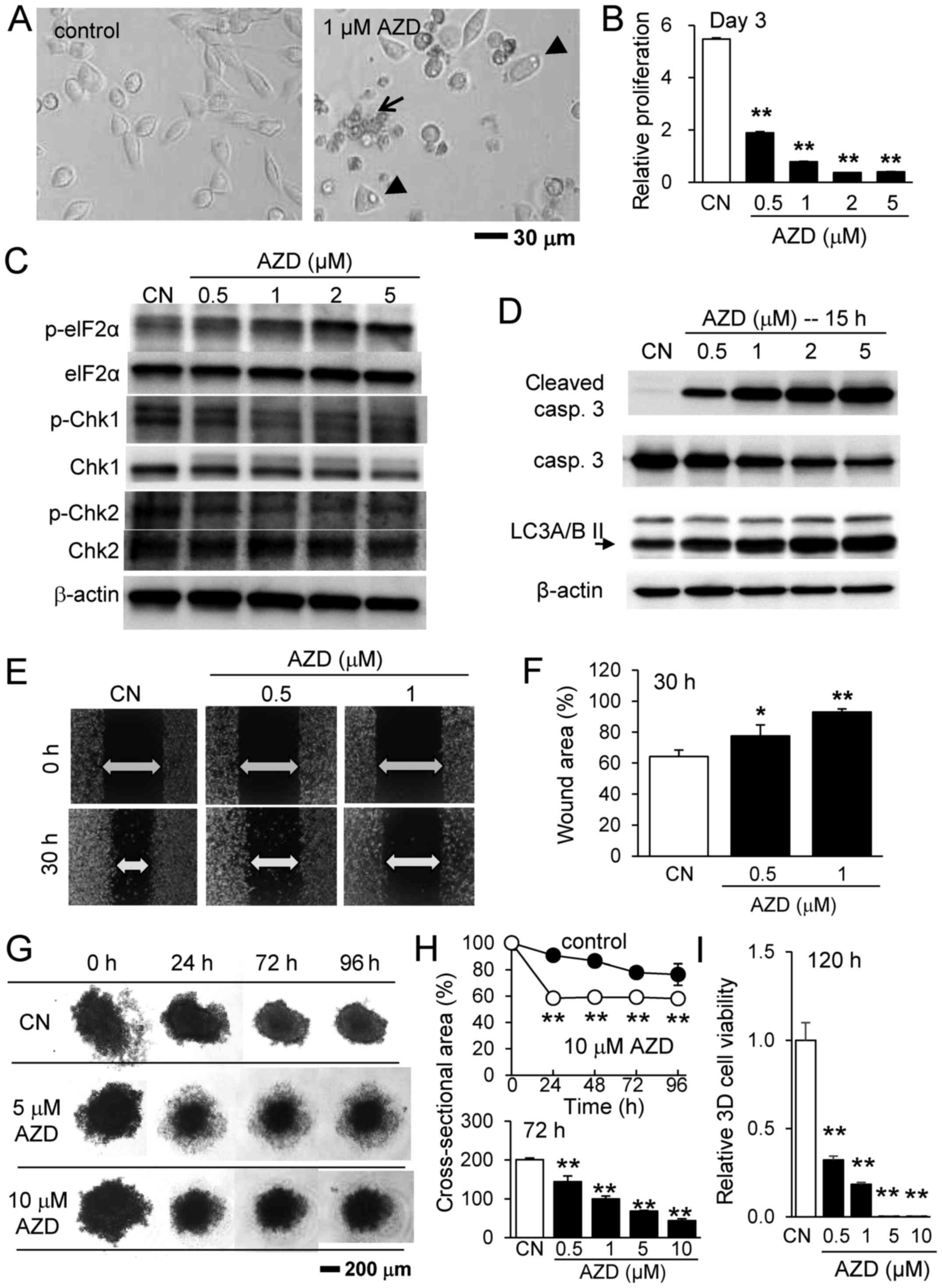
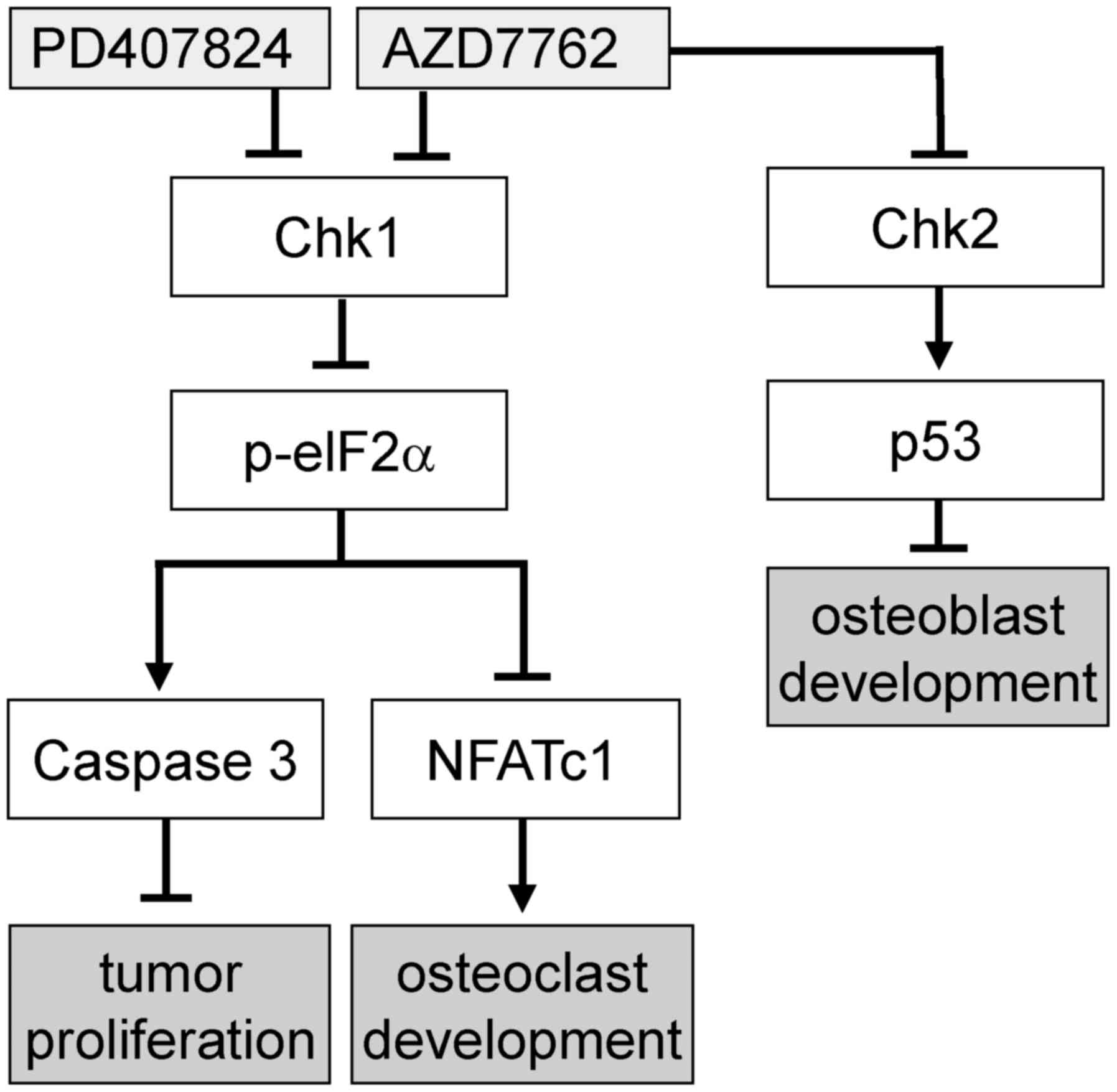
The Chk1/2 inhibitor AZD7762 sensitizes SW480 colon cancer cells to... | Download Scientific Diagram
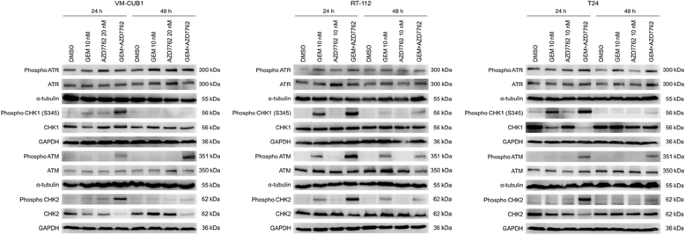
Checkpoint kinase inhibitor AZD7762 strongly sensitises urothelial carcinoma cells to gemcitabine | Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research | Full Text

Combination Treatment of VE-821 and AZD7762 Results in S Phase Arrest... | Download Scientific Diagram

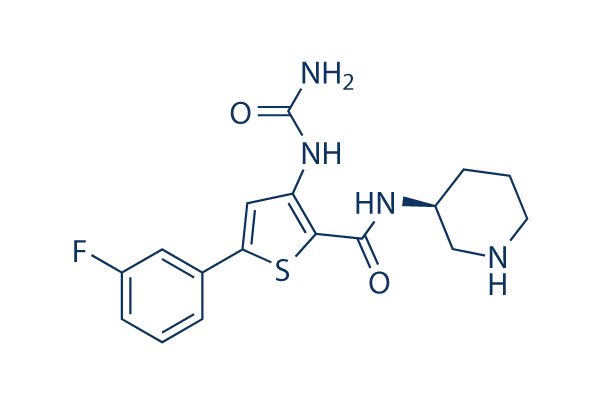
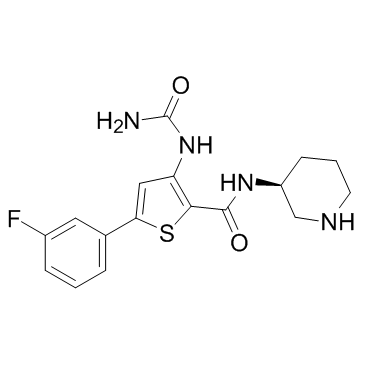
5 (3 Fluorophenyl) N (3 Piperidinyl) 3 Ureido 2 Thiophenecarboxamide - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics

Effect of AR Knockdown and Chk1/2 Inhibitor AZD7762 on TopBP1-ATR-Chk1... | Download Scientific Diagram

Discovery of Checkpoint Kinase Inhibitor (S)-5-(3-Fluorophenyl)-N-(piperidin-3-yl)-3-ureidothiophene-2-carboxamide ( AZD7762) by Structure-Based Design and Optimization of Thiophenecarboxamide Ureas | Journal of Medicinal Chemistry
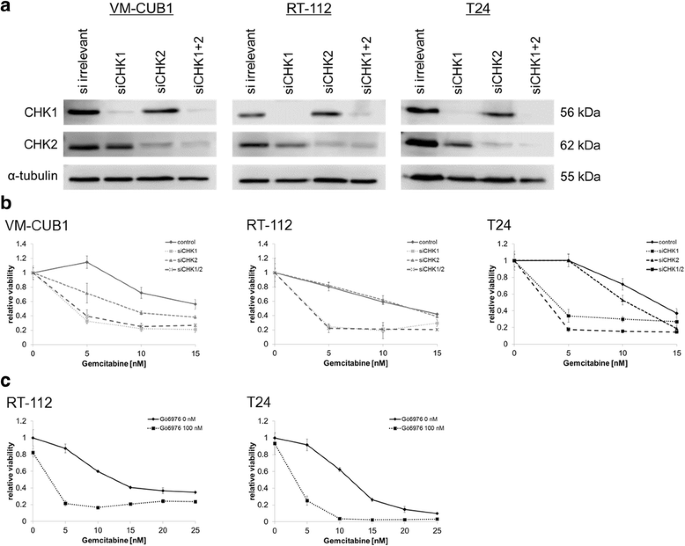
Checkpoint kinase inhibitor AZD7762 strongly sensitises urothelial carcinoma cells to gemcitabine | Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research | Full Text
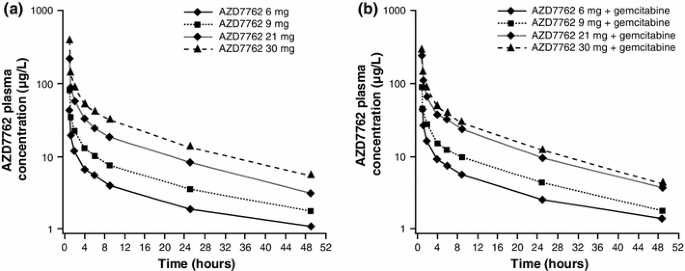
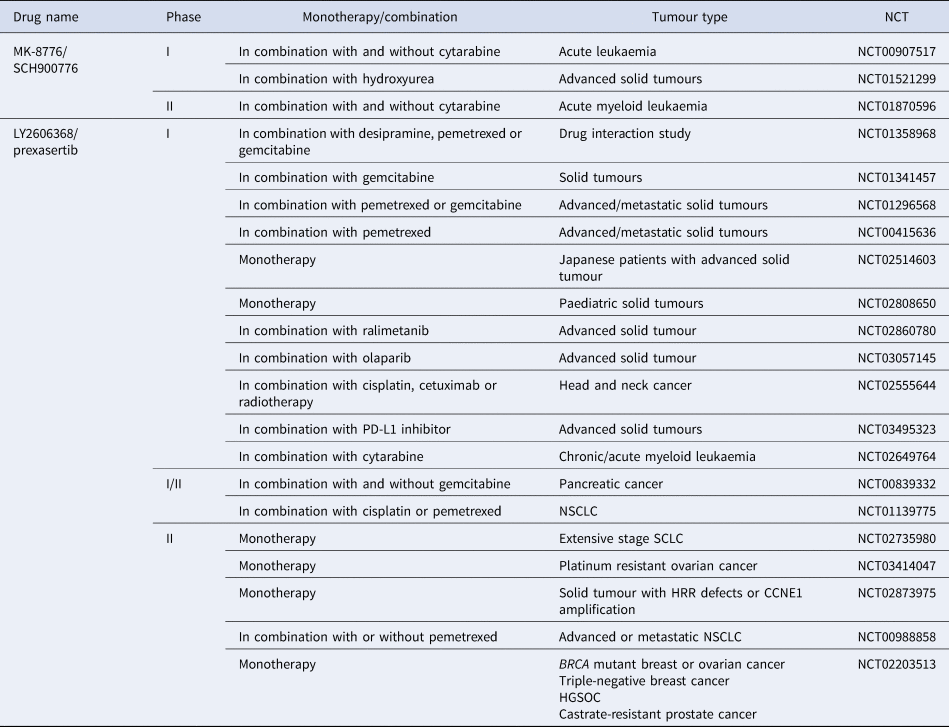
Phase I, dose-escalation study of AZD7762 alone and in combination with gemcitabine in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumours | SpringerLink

IJMS | Free Full-Text | Crystal Structure of the Kinase Domain of MerTK in Complex with AZD7762 Provides Clues for Structure-Based Drug Development | HTML

Phase I, dose-escalation study of AZD7762 alone and in combination with gemcitabine in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumours | SpringerLink
Phase I Dose-escalation Study Of AZD7762, A Checkpoint Kinase Inhibitor, In Combination With Gemcitabine In Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors. | ApconiX
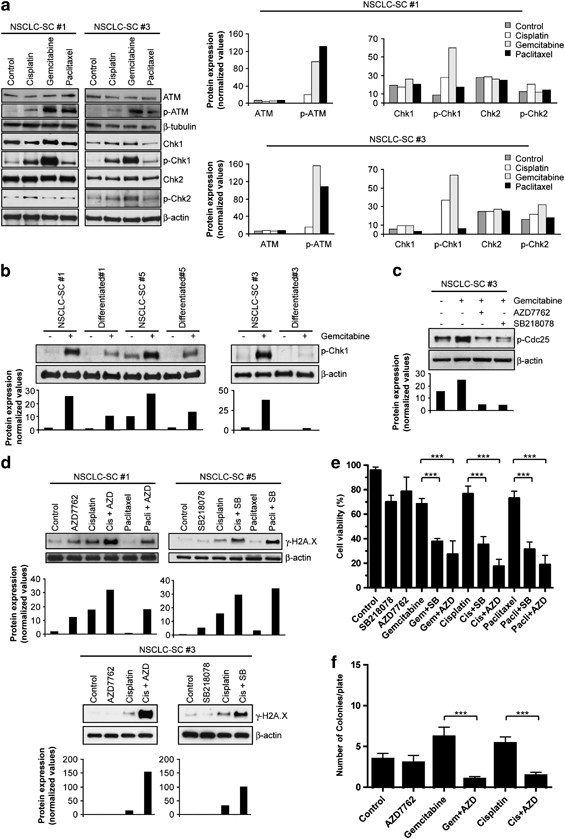
Therapeutic targeting of Chk1 in NSCLC stem cells during chemotherapy | Cell Death & Differentiation
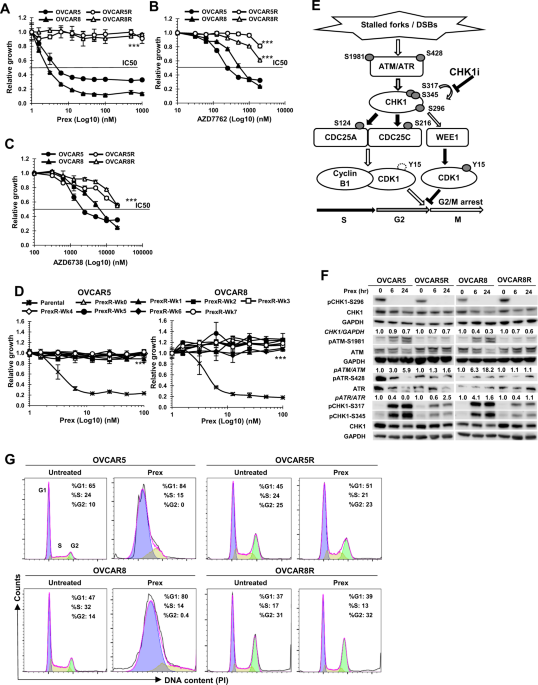
Resistance to the CHK1 inhibitor prexasertib involves functionally distinct CHK1 activities in BRCA wild-type ovarian cancer | Oncogene

Mechanism of radiosensitization by the Chk1/2 inhibitor AZD7762 involves abrogation of the G2 checkpoint and inhibition of homologous recombinational DNA repair. - Abstract - Europe PMC

ATR Target Activation by the CHK1 Inhibitor AZD7762 in U2OS Cancer Cells | Download Scientific Diagram